Lemongrass
Origin: Africa, Asia (tropical & subtropical), Australasia
Family: Poaceae
Subfamily: Panicoideae
Supertribe: Andropogonodae
Tribe: Andropogoneae
Subtribe: Andropogoninae
Scientific Name: Cymbopogon spp.
Indigenous (Noongar) Names: Djerp (C. ambiguus); djiraly (C. obtectus)
Folk Names: Sweet root
Magical
Element: Air
Day: Wednesday
Planet: Mercury
Zodiac: Gemini
Parts used: Leaf, essential oil
Magical Properties: Psychic awareness, cleansing, lust, protection, peace, divination, consecration, grounding
Substitutions: Lemon
Magical Uses
- Plant lemongrass around the home to protect from snakes.
- Make a potion with lemongrass to promote psychic powers.
Aromatherapy
Part Used: Leaves
Extraction Method: Steam distillation
Flash Point: 71°C
Scent Type: Citrus
Perfume Note: Middle/top
Scent Description: Fresh, grassy, lemony
Active Constituents: Citral (65–85%)
Aromatherapeutic Use
Uplifting, stimulating, revitalising. Insect repellent.
Blends well with: Basil, cedar, lavender, tea-tree
Warnings:
- Avoid during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
- Can cause skin irritation: Use only in low dilutions.
Medicinal
Note: This information is provided for informational purposes only, do not use any plants medicinally without consulting with an appropriate medical professional.
Medicinal Properties: Analgesic, antibacterial, anticatarrhal, antifungal, antipyretic, antiseptic, carminative, stimulant
Active Constituents: Citral (65–85%), myrcene, citronellal, citronellol, linalool and geraniol
Indigenous/Traditional Medicinal Uses (of various species):
- Decoctions of the whole plant were used as a wash for cramps, sores, rashes, earaches, and sore eyes, as well as general illness.
- Small amounts of the decoction were drunk to relieve sore throats and diarrhoea.
- The leaves were crushed to inhale the vapour to ease chest complaints.
- A decoction of the crushed leaves was drunk to treat coughs and colds, and rubbed on the body to ease sore muscles and headaches.
Warnings:
- Lemongrass seems to be able to trigger menstruation, potentially causing miscarriage, so should be avoided if pregnant.
Botanical
There are 53 different species of Cymbopogon. Of these, some of the most common are: Cymbopogon citratus (West Indian lemongrass) is the primary kind from South-East Asia, used in cooking and for essential oil; C. flexuosus (East Indian lemongrass) is also used to produce essential oil; C. ambiguus (Australian lemon-scented grass) is the most common Australian species that the name ‘lemongrass’ is applied to.
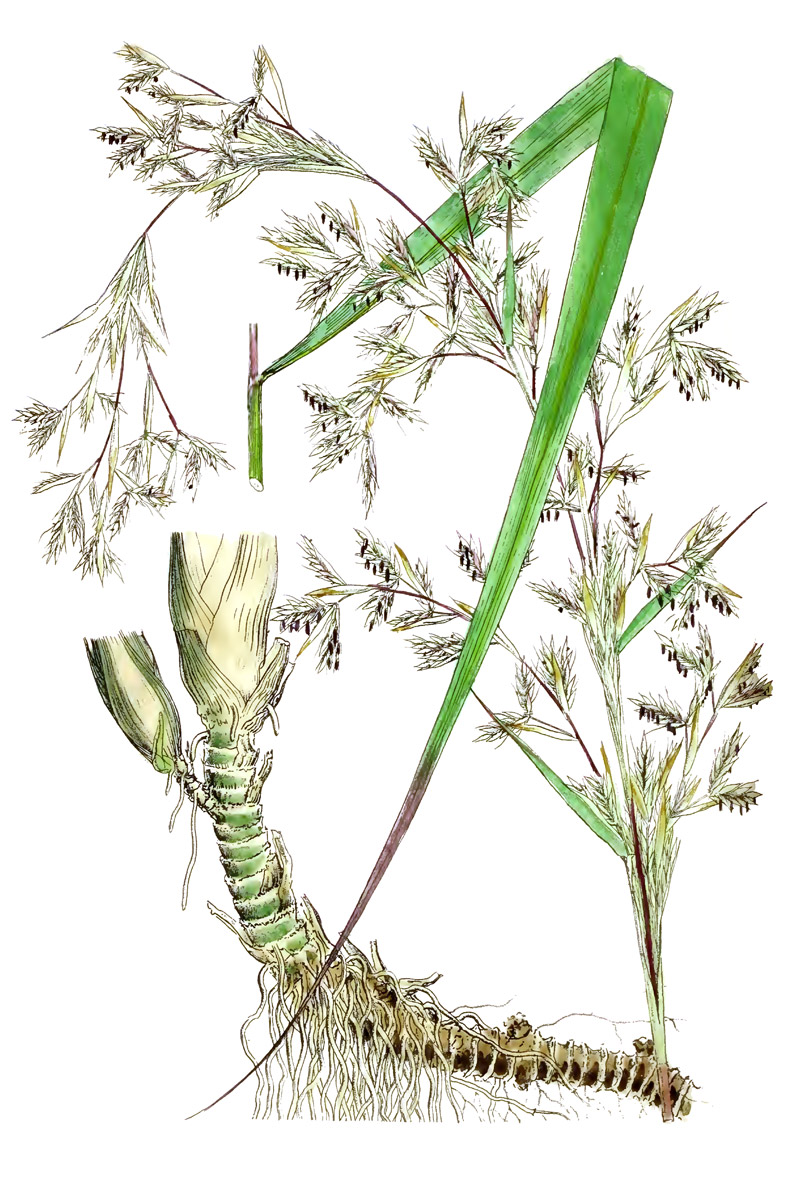
Type: Grass
Plant Height: 1m-2m
Leaves: Long, thin, yellow-green leaves (up to 1m long), sometimes with a slightly rough texture
Etymology: The genus name comes from the Greek words kymbe (boat) and pogon (beard), in reference to the boat-shapes spathes the flower spikelets emerge from. ‘Lemongrass’ is in reference to the grasses' fragrance.
In the Garden
Type: Perennial
Sow: Spring
Light: Full sun
Water: Keep moist
Soil: Well-drained
Companion Planting: Basil, coriander, echinacea, lemon verbena, marigold, mint, thyme
Tips:
- Allow the plant to develop thick stems before harvesting.
- Cut back well to encourage more growth.
- Mulch well to keep the roots warm over winter.