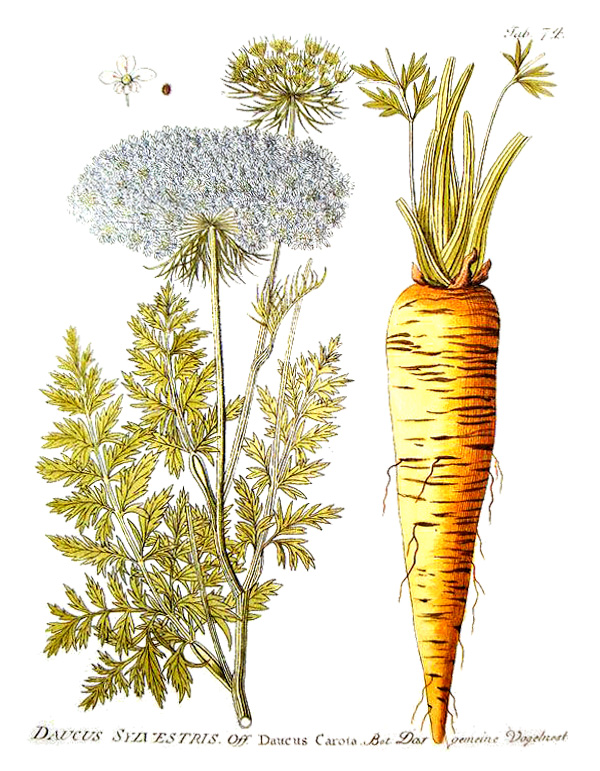
Carrot

Origin: Central Asia, but spread around much of Europe/Asia by 2-3000 BCE
Family: Apiaceae
Subfamily: Apioideae
Tribe: Scandiceae
Subtribe: Daucinae
Scientific Name: Daucus carota
Folk Names: Bee’s nest, bird’s nest, bishop’s lace, philtron (Old Greek), Queen Anne’s lace
Magical
Element: Fire
Day: Wednesday
Planet: Mercury
Zodiac: Virgo
Parts used: Root, seeds
Magical Properties: Fertility, sexuality, healing, lust
Lore
- Nicholas Culpeper states that carrots belong to Mercury. Among other uses, it’s suggested that eating the root promotes gas, which is expelled by eating the seeds.
Magical Uses
- Eating carrot seeds is said to promote pregnancy.
- Eating carrots is said to promote lust and help against impotence.
Aromatherapy
Part Used: Seeds
Extraction Method: Steam distillation
Flash Point: 54°C
Scent Type: Herbaceous
Perfume Note: Middle
Scent Description: Herbaceous, earthy, and slightly spicy
Aromatherapeutic Use
Blends well with: Bergamot, juniper, lavender, citrus
Warnings:
- Avoid during pregnancy.
Botanical
The domestic carrot is the subspecies sativus, which has been selectively bred for its larger and less woody taproot.
Wild carrot is very similar in appearance to poison hemlock.
Type: Biennial herb
Plant size: 30-60cm
Leaves: Finely-divided, lacy leaves
Flowers: Small, white flowers in dense umbels 8-10cm across, occasionally with a red or purple-ish flower in the centre
Etymology: The word carrot has been traced back to the Indo-European root ker (horn), in reference to its horn-like shape. In Old English, the carrot (which was whiter in colour) was not distinguished linguistically from parsnips - they were called moru/more (from the Proto-Indo-European mork, for “edible root”).
In the Garden
Type: Root vegetable
Sow: Spring/summer/autumn
Light: Full sun to partial shade
Soil: Light, well-draining soil
Companion Planting: Rosemary, sage, chives, lettuce, leek, onions, peas, tomato
Tips:
- Carrot seedlings are particularly vulnerable to slugs.
- Can be harvested year-round.
- Carrots are generally ready to harvest 3-4 months after planting.