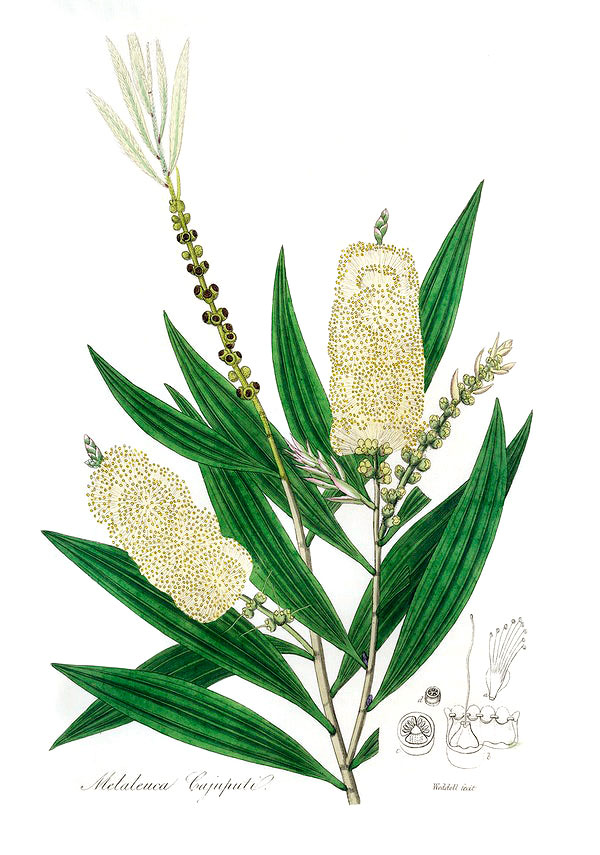
Cajeput

Origin: Australia & South-East Asia
Family: Myrtaceae
Subfamily: Myrtoideae
Tribe: Melaleuceae
Scientific Name: Melaleuca cajuputi
Folk Names: Swamp tea tree, white tea tree
Magical
Element: Earth
Direction: East
Days: Saturday
Planet: Saturn
Zodiac: Capricorn
Magical Properties: Healing, protection, balance, courage, creativity, sexuality, grounding
Substitutions: Niaouli, tea tree, eucalyptus
Aromatherapy
Part Used: Leaves and twigs
Extraction Method: Steam distillation
Flash Point: 46°C
Scent Type: Woody
Perfume Note: Middle/top
Scent Description: Fresh, camphoraceous
Aromatherapeutic Uses
Stimulating, helps with mental focus, and can be used to ease colds/flus and congestion. Repels insects.
Warnings:
- Use with caution around children: Cajeput oil can be high in 1,8-cineole (the main compound in eucalyptus oil), which can affect the autonomic nervous system in children, causing suffocation.
- Can cause skin irritation: use only in low dilutions.
Medicinal
Active Constituents: Up to 60% 1,8-cineole (the main compound in eucalyptus oil), which is responsible for the anti-microbial effects.
Medicinal Properties:
- Anti-bacterial
- Anti-fungal
- Anti-septic
- Decongestant
Indigenous/Traditional Medicinal Uses:
- The strong aroma is used to treat headaches, sinusitis, respiratory problems, coughs, stomach upsets, and rheumatic aches and pains.
- A tea made from the herbs was used in Thailand to treat a range of medical problems.
Practical
In Southeast Asia, it is used as a fuel, and for making charcoal. The timber has been used in construction for supporting columns, frames, and floorboards for houses, as well as for fences.
The bark has been used in Indonesia as a roofing material, and sealant in boat construction.
Indigenous Uses:
- Some flowers produce a honey-like nectar, which was eaten, or made into a drink by soaking the flowers in water.
- Bark was used as a container for food and water, to wrap food for cooking in coals or an earth oven.
Botanical
Type: Evergreen tree
Plant size: Usually up to 35m
Bark: White/grey/beige papery bark
Leaves: Flat, leathery, dull-green leaves, 4-14cm long and 1-6cm wide
Flowers: Spikes comprised of 8-20 groups of 3 flowers with white/cream stamens; branches continue growing out past the flowers.
Fruit: Cup-shaped, woody capsules, 2-3mm long, and clustered along the spike. Seeds are released annually.
Etymology: Cajeputi is suspected to be a corruption of the Indonesian name for the plant, “kayu putih” (which means ‘white wood’).